
EMT in WPT
Our Team
- Darshan S
- Rishee K
- Ritik Kumar Mehta
- Sakshi Chavan
- Sudhaharan S J
EMT in WPT
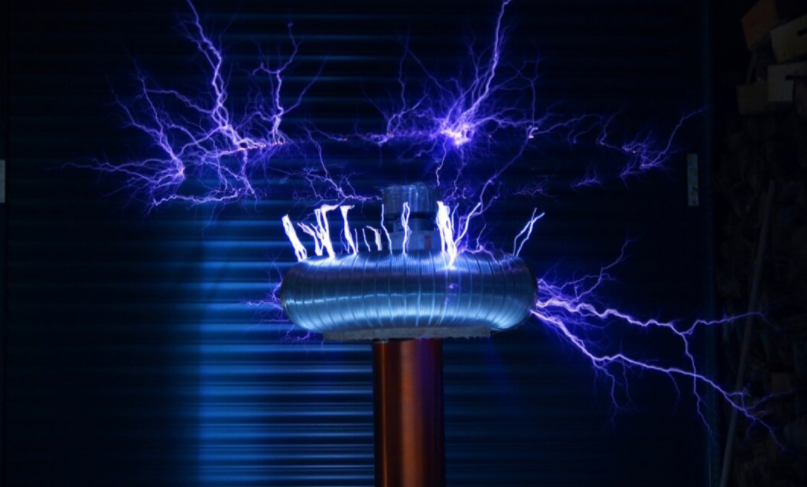
Resonant Inductive Coupling :-
The resonant inductive coupling is the
near field wireless transmission of electrical energy between magnetically coupled coils, which is part of a resonant circuit tuned to resonate at the same frequency as the driving frequency. A magnetic resonance coupled wireless power transmission is using the principle of resonance to set corresponding transmitting device and receiving device-related parameters, therefore promoting the transmit coil, the corresponding receiving coil, and the overall system is in the same resonant frequency (i.e. to achieve "electrical resonant" state) to make a corresponding energy-efficient transmission. Magnetic resonance coupled wireless power transmission systems are mainly realized by the high-frequency AC power supply, the resonance coil, the rectifying filter circuit, and the compensation network structure of the receiving and transmitting end. The improvement of each part can achieve the high power, high efficiency, and long-distance transmission of the whole system.
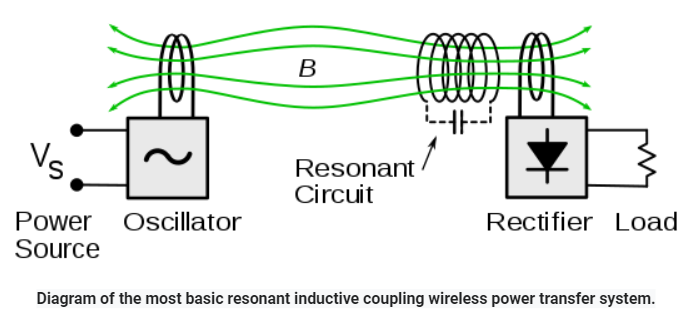
This process occurs in a resonant transformer, an electrical component that consists of a high Q coil wound on the same core with a capacitor connected across a
coil to make a coupled LC circuit. The most basic resonant inductive coupling consists of one
drive coil on the primary side and one resonance circuit on the secondary side. In this case, when the resonant state on the secondary side is observed from the primary side, two resonances as a pair are observed. One of them is called the antiresonant frequency (parallel resonant frequency 1), and the other is called the resonant frequency (serial resonant frequency 1'). The short-circuit inductance and resonant capacitor of the secondary coil are combined into a resonant circuit. When the primary coil is driven with a resonant frequency (serial resonant frequency) of the secondary side, the phases of the magnetic fields of the primary coil and the secondary coil are synchronized. As a result, the maximum voltage is generated on the secondary coil due to the increase of the mutual flux, and the copper loss of the primary coil is reduced, the heat generation is reduced, and the efficiency is relatively improved.

A resonant Inductive coupling is an effective solution for the problems associated with non-resonant Inductive wireless power transfer systems because especially the efficiency of power transmission depends on the distance between the coils. In the resonance concept, the power between the coils can be transferred efficiently even if the distance between the coils is a few meters.



